nenuphar_cli
Nenuphar Documentation
Nenuphar is a tool to generate Swagger OpenAPI documentation for Dart Frog projects.
Generate your OpenAPI documentation in few steps:
Table of contents
- Installation
- Initialize nenuphar
- Generate openapi definition file
- Declare resources components
- Allowed methods
- Parameters
- Security
- Start your Dart Frog server
- Enjoy 🎉
Dart Frog
Dart Frog is a minimalistic backend framework for Dart made by VGVentures.
Create a new Dart Frog project
To create a new Dart Frog backend project, run the following command:
dart pub global activate dart_frog_cli
dart_frog create <project name>
Swagger OpenAPI
Swagger is a set of open source tools built around the OpenAPI Specification that can help you design, build, document and consume REST APIs.
OpenAPI Specification
The OpenAPI Specification (OAS) defines a standard, language-agnostic interface to RESTful APIs which allows both humans and computers to discover and understand the capabilities of the service without access to source code, documentation, or through network traffic inspection.
Please visit https://swagger.io/specification/v3/ for more information.
Swagger UI
Swagger UI allows anyone — be it your development team or your end consumers — to visualize and interact with the API’s resources without having any of the implementation logic in place. It’s automatically generated from your OpenAPI (formerly known as Swagger) Specification, with the visual documentation making it easy for back end implementation and client side consumption.
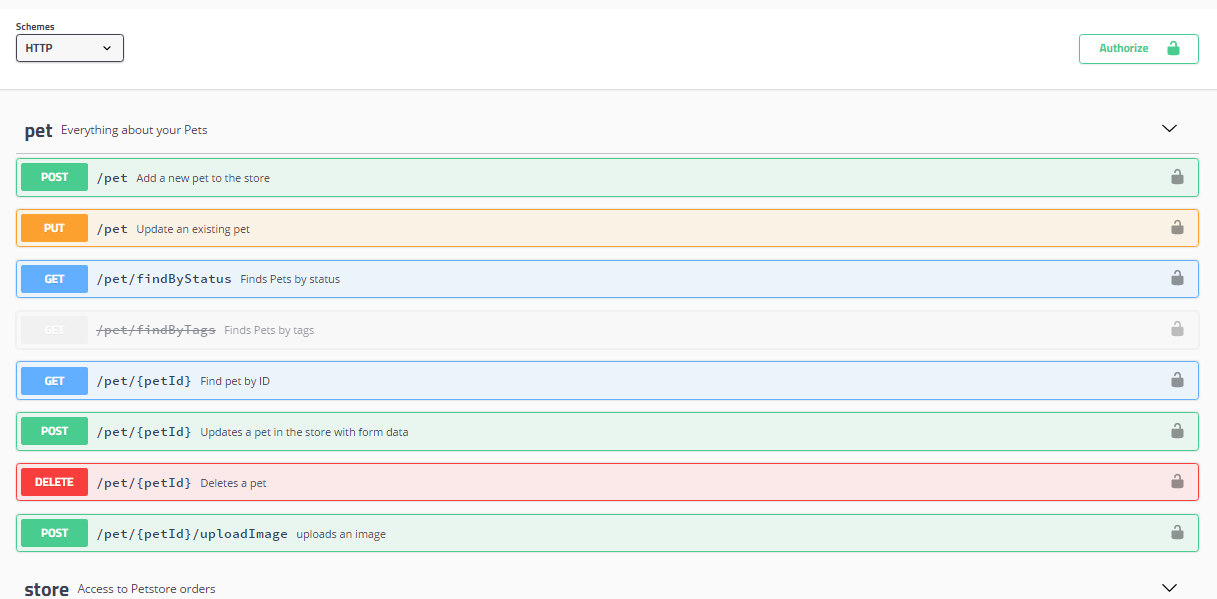
Please visit https://swagger.io/tools/swagger-ui/ for more information.
Nenuphar

Installation
dart pub global activate nenuphar_cli
Initialize nenuphar
First you need to initialize your project by running the following command in the root of your project:
nenuphar init
Index.html file
Init command will create new file public/index.html. This file will be served statically by your Dart Frog server to expose your Swagger UI documentation.
nenuphar.json file
Init command will create new file nenuphar.json. This file contains the base configuration of your openapi documentation.
Feel free to edit this file with your own configuration.
{
"openapi": "3.0.3",
"info": {
"title": "A sample API",
"description": "A sample API",
"termsOfService": "http://localhost",
"contact": {
"name": "none",
"url": "http://localhost",
"email": "none@api.com"
},
"license": {
"name": "",
"url": ""
},
"version": "0.0.0"
},
"externalDocs": {
"description": "",
"url": "http://localhost/"
},
"servers": [
{
"url": "http://localhost:8080",
"description": "Local server"
}
],
"paths": {}
}
Init failures
Error: index.html already exists
init command will fail if the public/index.html file already exists and the --override option is not set to true.
Error: nenuphar.json already exists
init command will fail if the nenuphar.json file already exists and the --override option is not set to true.
init command available options
| Option | Abbr | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
| –url | -u | Url to the openapi definition file | http://localhost:8080/public/openapi.json |
| –override | -o | Override existing file | false |
Generate openapi definition file
Nenuphar scans your Dart Frog project to generate an OpenAPI definition file. Each route will generate the CRUD operations documentation for the exposed resource.
NOTICE:
nenuphar ignores the
/route by default.
First create a Dart Frog route:
dart_frog new route "/todos"
Then generate the OpenAPI definition file
nenuphar gen
gen failures
Error: Init not called
gen command can fail if you didn’t call the nenuphar init command before.
gen command available options
| Option | Abbr | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
| –output | -o | Output file | public/openapi.json |
The openapi specification will be written in the public/openapi.json file.
This file is loaded by the public/index.html file to display the documentation.
NOTICE:
You need to run the nenuphar gen command each time you update your API.
Watch mode
nenuphar can watch your Dart Frog project to automatically generate the openapi definition file each time you update a route.
nenuphar watch
This command will use the dart_frog daemon to watch your route modifications using the command dart_frog daemon
Resources components
To declare any resource component, you need to create a json file in the components/ folder using the same name as the resource.
For example, if you want to declare a Todo resource for the /todos path, you need to create a components/todos.json file.
Declare a resource
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "integer",
"format": "int64"
},
"name": {
"type": "string"
},
"completed": {
"type": "boolean"
}
}
}
See OpenAPI schema object specification for more information.
Allowed methods
By default, nenuphar generates the documentation for the following methods:
- OPTIONS
- GET
- HEAD
- POST
- PUT
- PATCH
- DELETE
You can override this behavior by adding the @Allow tag to your documentation comment. This tag will only allow the specified methods.
The example below will only allow the GET and POST methods.
/// @Allow(GET, POST)
Future<Response> onRequest(RequestContext context) async {
// ...
}
Parameters
Header
Nenuphar searches a specific documentation comment in your Dart Frog route to generate the header parameters.
Add the @Header tag to your documentation comment to generate the header parameter.
The name of the parameter is the value of the @Header tag.
/// @Header(Authorization)
Future<Response> onRequest(RequestContext context) async {
// ...
}
Query
Nenuphar searches a specific documentation comment in your Dart Frog route to generate the query parameters.
Add the @Query tag to your documentation comment to generate the header parameter.
The name of the parameter is the value of the @Query tag.
/// @Query(completed)
Future<Response> onRequest(RequestContext context) async {
// ...
}
Path
Path parameters are automatically detected by nenuphar using the Dart Frog Dynamic routes system
Body
Body parameters are generated using the Resource components declared in the components/ folder.
Security
If your API is secured, you can declare the security schemes and use them in your paths.
Declare security schemes
To declare a security scheme, you need to create a _security.json file in the components/ with the appropriate content.
Supported security schemes are basic, apiKey and oauth2.
{
"todos_basic_auth": {
"type": "http",
"scheme": "basic"
},
"todos_api_key": {
"type": "apiKey",
"name": "api_key",
"in": "header"
},
"todos_oauth": {
"type": "oauth2",
"flows": {
"implicit": {
"authorizationUrl": "https://nenuphar.io/oauth/authorize",
"scopes": {
"write:todos": "modify todos",
"read:todos": "read your todos"
}
}
}
}
}
Use security in path
To use a security scheme in a path, you need to add the @Security tag to your documentation comment.
The name of the security scheme is the value of the @Security tag.
/// @Security(todos_basic_auth)
Future<Response> onRequest(RequestContext context) async {
// ...
}
Use scopes in path
To use a scope in a path, you need to add the @Scope tag to your documentation comment.
The name of the scope is the value of the @Scope tag.
/// @Security(todos_oauth)
/// @Scope(read:todos)
Future<Response> onRequest(RequestContext context) async {
// ...
}
Start your Dart Frog server
You’re now ready to start your Dart Frog server
dart_frog dev
Visit http://localhost:8080/index.html to see your documentation.
open http://localhost:8080/index.html
Enjoy 🎉
Thanks for using Nenuphar!

